If your current study routine involves endlessly rereading a textbook and hoping the information magically sticks—you’re not alone. But this method, especially in graduate school, often leads to frustration, stress, and information overload. The truth is, what worked in high school or even undergrad may no longer cut it in the rigorous world of advanced education.
To truly thrive in grad school, it’s essential to adopt study strategies that promote long-term retention, deeper understanding, and efficient time management. Below, we’ll explore ten of the most effective study techniques—plus a few preparatory habits—to help you elevate your learning game and maximize your academic performance.
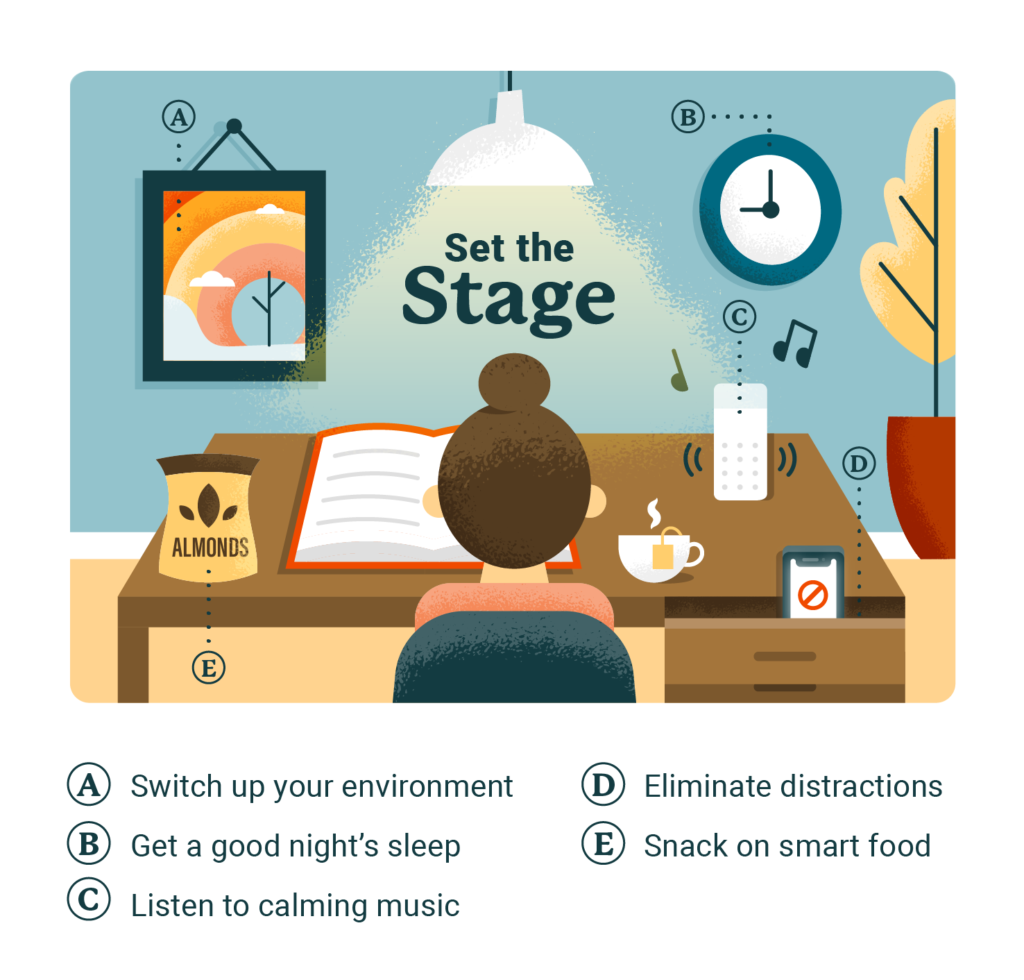
Start with the Right Environment
Before diving into any study technique, it’s critical to optimize your physical and mental setting. The best strategies won’t help much if your brain isn’t primed to absorb new information.
- Prioritize Sleep: Consistent sleep is more beneficial than just getting eight hours before an exam. Quality rest over several days strengthens memory consolidation.
- Vary Your Study Spaces: Changing your environment can stimulate your brain and enhance recall. Study at a quiet café, in a library nook, or even outdoors for a fresh mental boost.
- Eliminate Distractions: Turn off notifications, silence your phone, and create boundaries from social media during focused study time.
- Fuel Your Brain Wisely: Avoid sugar crashes by opting for healthy snacks like nuts, apples, or protein-packed edamame.
- Listen Smart: Lo-fi beats or instrumental music can help improve focus, while lyrical tracks may disrupt your concentration.
1. The SQ3R Method
This classic reading strategy—Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review—encourages active engagement with material. Rather than passively reading chapters, you start by skimming the content to get an overview, form questions to guide your reading, and finish by summarizing and reviewing. It’s especially effective for dense or technical texts.
2. Retrieval Practice
Instead of rereading, challenge yourself to recall information without looking at your notes. The act of remembering strengthens memory pathways far better than passive review.
- Use practice quizzes and flashcards.
- Write down answers rather than mentally checking them.
- Teach others or explain concepts aloud.

3. Spaced Repetition
Cramming might feel productive, but spacing out your study sessions is far more effective. This method taps into the brain’s ability to retain information by reinforcing it just as it starts to fade.
A sample schedule:
- Day 1: Learn the material
- Day 2: Review
- Day 3: Reinforce again
- 1 week later: Review
- 2 weeks later: Final reinforcement
Planning ahead ensures better retention—and less stress when exams roll around.
4. The PQ4R Method
Another structured reading strategy, PQ4R stands for: Preview, Question, Read, Reflect, Recite, Review. It extends SQ3R by adding a reflection stage, encouraging deeper thinking about the material and fostering critical analysis.
5. The Feynman Technique
Named after physicist Richard Feynman, this method involves explaining complex topics in plain language—as if teaching a beginner. If you can’t simplify a concept, you likely don’t understand it well enough. This method reveals knowledge gaps and pushes you to truly own the material.
How to do it:
- Write the topic at the top of a page.
- Explain it simply, using your own words.
- Identify gaps and clarify misunderstandings.
- Refine and simplify the explanation further.

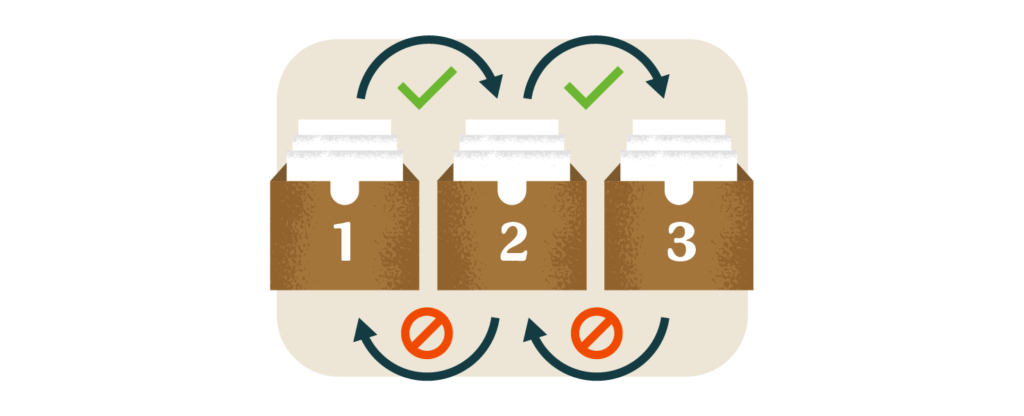
6. The Leitner System
This flashcard-based approach organizes cards into boxes based on how well you know each one. Cards you get right move to the next box and are reviewed less frequently. Those you miss stay in the first box for daily review. It’s a smart, adaptive way to focus on your weak spots.

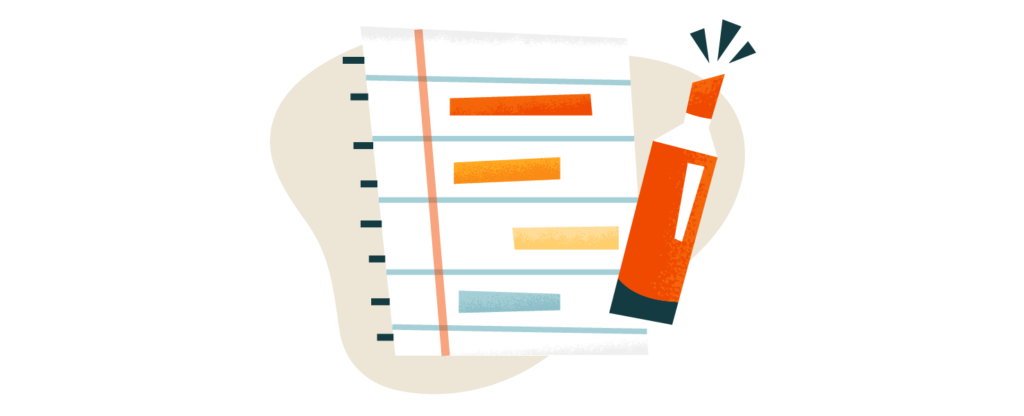
7. Color-Coded Notes
Color isn’t just aesthetic—it enhances learning. Red for key points, yellow for highlighting critical information, and different hues for organizing categories can make notes more engaging and easier to digest. Just avoid turning your pages into a rainbow—be selective and strategic.

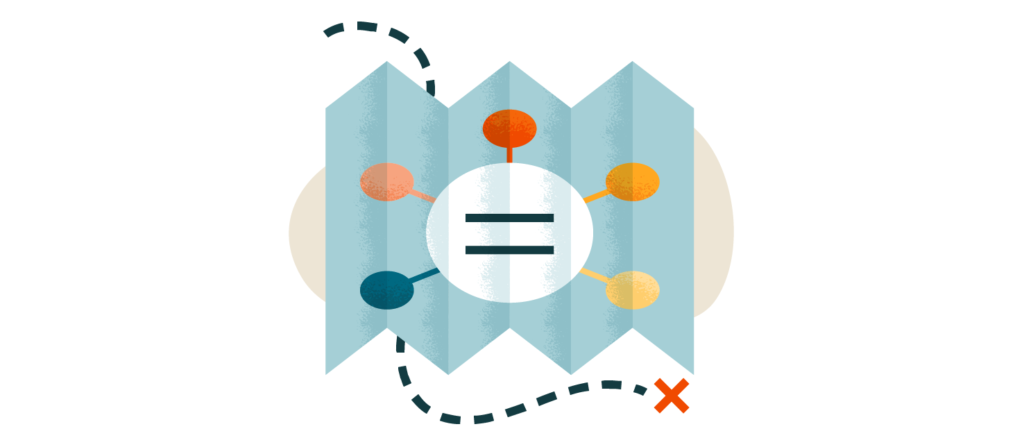
8. Mind Mapping
Perfect for visual learners, mind maps transform linear notes into visual diagrams. Start with your central topic, branch out to subtopics, and keep adding layers. Use colors, arrows, and images if it helps you make associations. It’s a fantastic way to see how ideas interconnect and to recall big-picture themes during exams.

9. Exercise Before Studying
A short burst of physical activity—whether it’s a jog, yoga session, or brisk walk—can dramatically improve brain function. It boosts focus, energy, and mood by increasing blood flow and releasing endorphins, preparing you for more productive study sessions.
10. Review Before Bed
Sleep is when the brain consolidates memories. By reviewing your material right before bed, you enhance the likelihood of remembering it the next day. Think of it as giving your brain a final input to process overnight.

Final Thoughts
Studying smarter—not harder—is the key to graduate-level success. These techniques aren’t one-size-fits-all, so try experimenting to see which ones suit your learning style best. Whether you’re preparing for a major exam or just trying to keep up with the demands of your coursework, implementing even a few of these strategies can dramatically improve your retention, reduce your stress, and sharpen your academic performance.
Remember, consistency and curiosity are your greatest tools. With the right approach, studying doesn’t have to be a chore—it can become an empowering, enlightening part of your grad school journey.





